ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
(3D Printing)
Introduction:
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing is a revolution in industrial production that enables the creation of lighter, stronger parts and systems.
It is a technological advancement in manufacturing field made possible by converting from traditional methods to digital processes. In recent decades, communications, imaging, architecture and engineering have all undergone their own digital revolutions. Now, AM can bring digital flexibility and efficiency to manufacturing operations.
Additive manufacturing or 3D printing deposits material layer by layer in precise geometric shapes following predetermined path to create a physical 3D object by utilizing data from computer-aided-design (CAD) software or 3D object scanners. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object. Alternatively, when you create an object by traditional means i.e. subtractive manufacturing which is cutting out or hollowing out material through milling, machining, carving, shaping or other means.
Although the terms “3D printing” and “rapid prototyping” are casually used to discuss additive manufacturing, each process is actually a subset of additive manufacturing. 3D printing and rapid prototyping are often confused as the same thing however they are some difference 3D printing is a method of additive manufacturing whereas rapid prototyping is an application of this technology.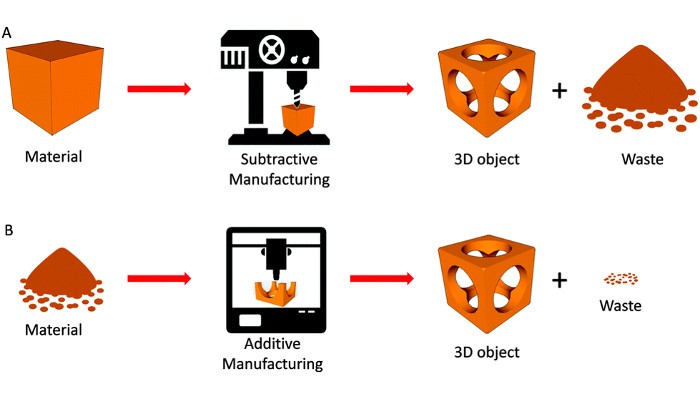
 Click to know more about us
Click to know more about us